When customers inquire about a building wire cable extrusion line, they typically need a high-speed, precision system for producing PVC-insulated or XLPE-insulated wires (e.g., THHN, THW, building wires per IEC 60227, UL 83, BS 6004). Below is a detailed breakdown of the extrusion line components, key specifications, and common customer concerns.
Building Wire Cable Extrusion Line: A Complete Guide for Manufacturers
In the construction and electrical industries, building wires are essential for power distribution, lighting, and safety systems. To produce high-quality building wires efficiently, manufacturers rely on cable extrusion lines—sophisticated systems that apply insulation (such as PVC or XLPE) onto copper or aluminum conductors.
This blog covers:
✅ Key components of a building wire extrusion line
✅ Production specifications & material options
✅ Common challenges & solutions
✅ How to choose the right extrusion line
1. What is a Building Wire Cable Extrusion Line?
A building wire extrusion line is an automated production system that:
- Extrudes insulation (PVC, XLPE, or LSZH) onto conductors.
- Ensures precise thickness & uniformity for safety compliance.
- Operates at high speeds (up to 600 m/min) for mass production.
Common building wire types produced:
- THHN/THWN (UL standard)
- PVC-insulated wires (IEC 60227)
- XLPE-insulated cables (BS 6004, VDE)
2. Key Components of the Extrusion Line
A. Pay-Off & Tension Control
- Unwinds bare conductors (copper/aluminum) smoothly.
- Critical feature: Automatic tension control to prevent wire breaks.
B. Extruder (Single or Twin-Screw)
- Melts & applies insulation (PVC, XLPE, or LSZH).
- Temperature control: 120–220°C (varies by material).
- Screw design: L/D ratio of 25:1 for optimal melting.
C. Cross-Head & Tooling (Die & Tip)
- Shapes insulation around the conductor.
- Tungsten carbide dies ensure precision (±0.02mm).
D. Cooling System
- Water baths or air cooling solidify insulation.
- Prevents bubbles & warping.
E. Capstan & Puller
- Maintains consistent speed (up to 600 m/min).
- Servo-controlled for smooth operation.
F. Marking & Testing
- Laser/inkjet printer for cable markings (size, voltage, manufacturer).
- Spark tester detects insulation defects (0–10kV).
G. Take-Up & Coiling
- Winds finished wire onto reels/drums.
- Automatic traverse for neat winding.
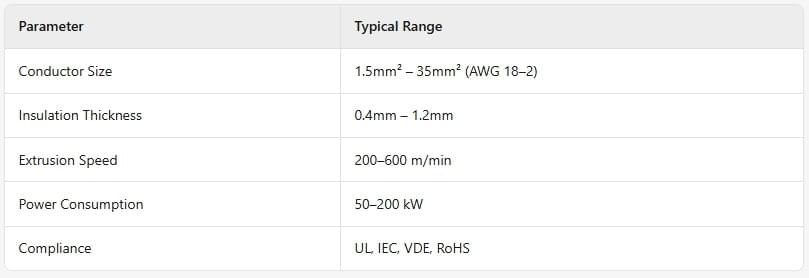
3. Production Specification
4. PVC vs. XLPE Extrusion: Which is Better?
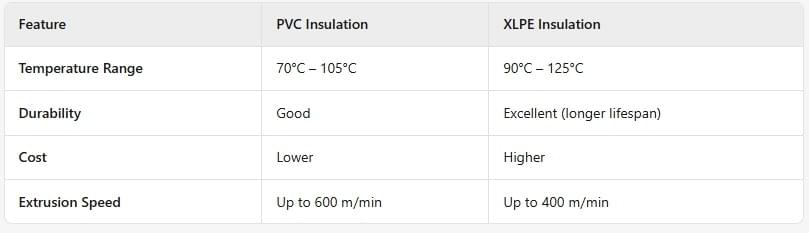
Best for:
- PVC: General-purpose wiring (low cost, flexible).
- XLPE: High-temperature & long-lasting applications.
5. Common Challenges & Solutions
Problem 1: Insulation Thickness Variation
✅ Solution: Use automatic gauge control (AGC) with laser sensors.
Problem 2: Bubbles in Insulation
✅ Solution: Pre-dry PVC/XLPE pellets & optimize cooling.
Problem 3: Low Production Speed
✅ Solution: Upgrade to high-speed servo-driven capstans.
Problem 4: Poor Marking Legibility
✅ Solution: Install high-resolution laser printers.
6. How to Choose the Right Extrusion Line?
When selecting a building wire extrusion line, consider:
✔ Production Speed (200 m/min vs. 600 m/min)
✔ Material Compatibility (PVC, XLPE, LSZH)
✔ Automation Level (manual vs. PLC-controlled)
✔ Compliance Needs (UL, IEC, VDE)
✔ After-Sales Support (warranty, spare parts availability)
Budget Range:
- Basic line: 30,000–200,000
- High-speed automated line: 100,000–300,000+
7. Conclusion: Why Invest in a Quality Extrusion Line?
A well-designed building wire extrusion line ensures:
🔹 High productivity (up to 600 m/min)
🔹 Consistent quality (precise insulation thickness)
🔹 Lower operational costs (energy-efficient motors)
🔹 Compliance with safety standards (UL, IEC, VDE)
Next Steps:
- Request a demo from manufacturers.
- Compare technical specs (screw design, cooling efficiency).
- Ask about customization (dual-layer extrusion, marking options).
Need help choosing the right extrusion line? Contact us for Max Xu-China wire machinery expert: cabletwister@126.com